The IT field always needs innovative means to add wings to the work capacity without investing any more on the new infrastructure, training new personnel, or licensing new software etc. which are various steps in the IT development. Cloud computing is one such technology which encompasses all these as mentioned above and extends IT’s existing work capabilities and hence got immense focus among the technocrats or technical society.
No doubt, these days, Cloud computing is at an early stage, with a diverse squad of large or small service providers delivering a swing of cloud-based services, start from full-blown applications to storage services to spam filtering and so on and so forth which is hoped to be enlarged in future. Looking at the pace of emergence of cloud computing aggregators and integrators, it is expected that, in the coming future, it will touch the height of the sky bringing a boom in the IT market.
Let’s see a through approach to the cloud computing covering introduction, architecture, usage, type, layers, characteristics, pros and cons and much more about this vast topic, Cloud Computing. This post will serve as a complete guide to the Cloud computing which will acknowledge you many things regarding Cloud Computing. We hope, this post will be appreciated by you. How do you feel the post, do not hesitate to share your thoughts with us; leave your comments in the comment area.
Introduction
Although Cloud Computing, the word seems to be quite small, but unlike the name, it covers a vast range and is regarded as the next big trend in the IT sector. When you will look over it from the perspective of IT professionals, you will find that, in real sense it fulfills a perpetual need of IT. Basically, the term Cloud computing describes a new supplement, consumption, and delivery model for IT services based on Internet protocols, which typically involves provisioning of dynamically scalable and often virtualized resources.
Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing as a service rather than a product, whereby shared resources, software and information are provided to computers and other devices as a utility over a network. Cloud computing provides computation, software, data access, and storage services that do not require end-user knowledge of the physical location and configuration of the system that delivers the services. To clarify your concept, you may consider example of electricity grid wherein end-users consume power without having any need to understand the component devices or infrastructure which are required to provide the service. Cloud computing providers deliver applications via the internet, which are in turn accessed from a Web browser, while the business software and data are stored on servers at a remote location.
Generally, Cloud Computing is a byproduct and consequence of the ease-of-access to remote computing sites provided by the Internet. It may be in the form of web-based tools or applications that users can access and use through a web browser as if they were programs installed locally on their own computers. Let us take a glance over the logical diagram of cloud computing.
Logical diagram of Cloud Computing
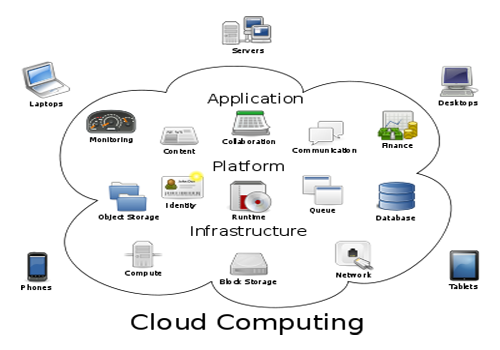
Types of Clouds
Now, you will see different types of clouds in cloud computing. Literally, there are four types of clouds: IaaS, SaaS, PaaS and Compute Clouds. We will discuss all these in details one by one.
1) Infrastructure as a Service Cloud (IaaS): IaaS is also referred to as Resource Clouds as it provides managed and scalable resources as services to the user or you can say that it provides enhanced virtualization capabilities. Data & Storage Clouds deal with reliable access to data of potentially dynamic size, weighing resource usage with access requirements and / or quality definition.
Examples: SQL Azure, Amazon S3
2) Platform as a Service Cloud (PaaS): It is another kind of cloud that typically makes use of dedicated APIs to control the behavior of a server hosting engine which executes and replicates the execution according to user requests and provides computational resources via a platform upon which applications and services can be developed and hosted. Since, individual API is exposed by each and every service provider according to the respective key capabilities, hence, applications developed for one specific cloud service provider cannot be moved to another cloud host. However, technical personnel are putting their efforts and are attempting to extend generic programming models with cloud capabilities.
Examples: Force.com, Google App Engine, Windows Azure (Platform)
3) Software as a Service (SaaS) Clouds: SaaS are sometimes referred to as Service or Application Clouds which provides applications or services using a cloud infrastructure or platform, rather than providing cloud features. This type of clouds offers implementations of specific business functions and business processes that are provided with specific cloud capabilities.
Examples: Google Docs, Salesforce CRM, SAP Business by Design
4) Compute Clouds: It is another important cloud type which typically offers the capability to provide computing resources. It provides access to computational resources, i.e. CPUs.
Examples: Amazon EC2, Zimory, Elastichosts
Usage of Clouds: Deployment types
As you have seen right before different types of clouds built in with different capability, it is sure that clouds may be hosted and employed in different fashions depending on their usability and hence the deployment of clouds. Based on the use case of clouds in various sectors, the deployment of the clouds can be categorized into following types which are mentioned a below:
1) Private Clouds: This cloud system provides more security and privacy, but is more expensive cloud solution in comparison to public cloud. Unlike public cloud, you need to set up your own data center and also bear all the installation & maintenance cost, and have complete control of all your data. In this kind, the functionalities are not directly exposed to the customer and are typically owned by the respective enterprise and or leased.
Example: eBay.
2) Public Clouds: This is the most popular type of cloud system and is considered as a main-stream cloud system by cloud computing experts. In public cloud system, a third party data center provides both disk space and computing power for all the application software.
In some cases you will find that, most of the enterprises use cloud functionality from others, and correspondingly offer their own services to users outside of their company. Such enterprises facilitates users with the actual capability to exploit the cloud features for fulfilling their purposes and also allows other enterprises to outsource their services to such cloud providers, reducing both costs as well as efforts to build up their own infrastructure. It is the case where clouds are deployed publicly and hence referred as public clouds.
Example: Amazon, Google Apps, Windows Azure.
3) Hybrid Clouds: Although public clouds allow enterprises to outsource parts of their infrastructure to cloud providers, at the same time they inhibit major drawbacks as they lose control over the resources and the distribution or management of code and data results some unwanted output to the enterprise respective; it is here where hybrid cloud deployment methods becomes handy to use. It is the fine blend of private and public cloud infrastructures to achieve maximum outsourcing and better results at the reduced costs while maintaining the desired degree of control over e.g. sensitive data by employing local private clouds.
Example: IBM, Juniper.
4) Community Clouds: Typically you see that, cloud systems are restricted to the local infrastructure. In other words we can say that once, the providers of public clouds offer their own infrastructure to customers they could actually resell the infrastructure of another provider, but here, clouds do not aggregate infrastructures to build up larger, cross-boundary structures. Here service providers can take advantage of this deployment method. Actually, Community clouds led different entities to contribute with their respective smaller infrastructure and have capability to aggregate either public clouds or dedicated resource infrastructures.
Example: Zimory, RightScale etc.
On the basis of use case, community clouds can be categorized into private and public community clouds.
I. Private Community Clouds: In this case, various smaller organizations come together to pool their resources for building a private community cloud.
II. Public Community Clouds: In this case, a big enterprise, e.g. Zimory, pool their cloud resources from different cloud providers and resell them
5) Special Purpose Clouds: When you will look over the functionality of IaaS and PaaS, you will find that IaaS clouds originating from data centers have a general purpose appealing as per their capabilities and hence can be equally used for a wide scope of use cases and customer types. In contrary to this, PaaS clouds tend to provide more specialized functionalities for specific use cases. Special Purpose Clouds are just extensions of “normal” cloud systems to provide additional, dedicated capabilities.
Example: Google App Engine
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
Likewise other technologies, Cloud Computing too have several advantage and disadvantage. It also has some advantages as well as disadvantages. Go through the below mentioned points to be aware of its advantage and disadvantage.
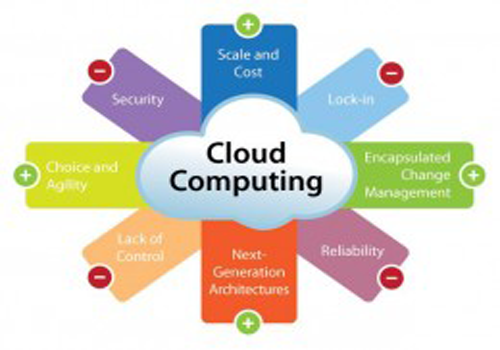
Advantage
1) Simplicity: Cloud computing has changed the game for entrepreneurs; the greatest part about it is its simplicity. Entrepreneurs have now enough on their plates as it is proving well in simplifying any part of their business operations. Also, hosting in the cloud can streamline and simplify actions such as “pass thru” billing to end-users etc.
2) Cost Effectiveness: Another plus point of Cloud Computing is that, it is cost effective to be used and implemented. Cloud hosting has a low cost of entry and no extra capital expenses are required for startup.
3) Fast start-up and product development: Cloud hosting is extremely fast to implement and supports multi-platform development environments. It allows you to test your business plan very quickly and moves as quickly as your business. Cloud computing is emerging technology which led to the faster product development without any extra capital expense. Cloud computing services allow a company to shift from capital to operational expenses even in do-or-die cases and created a buzz in the IT industry.
4) Scalability: Cloud computing has a huge future prospect, and when you talk in terms of scalability, it stands superb as you will get unlimited scalability.
5) Business agility: Cloud computing quickly solves your problems using IT resources; you have to wait no longer to get appropriate solutions. Really, the advent of Cloud computing has changed the whole pattern of business agility at a much lower cost.
Disadvantage
1) Performance: One of the major problems with the cloud computing technique is that the application performance may suffer. Actually what happens, in a cloud environment, all sites are competing for the hardware resources, and if multiple websites pierce inadvertently, it may cause chaos resulting in everyone slowing down. So when we take network latency into account, we find the performance of our applications suffers a lot.
2) Security: Cloud hosting does not provide you as much secure environment as you need. If anybody is looking to achieve and maintain data privacy requirements for PCI compliance, HIPAA compliance, SOX, E-commerce, and so on, then cloud hosting is not considered as the right solution.
3) Redundancy: One of the misconceptions of cloud hosting is that it’s hosted “in the sky and not in a datacenter,” which is not true. Cloud hosting resides in a single datacenter. Recently a large hosting provider’s data center went down leaving a lot of cloud hosted Web sites in the dark. The site owners had a huge reality check and quickly learned of the single-points of failure within a cloud environment.
4) Cost: One of the misconceptions of cloud hosting is that it is cost effective which is partially true. No doubt the cloud gives businesses a hands-free method to scale their hosting, however some problems may arise that are really financially surprising. There is a need to become quite attentive towards the clouds usage. Some usage methods won’t take your site to let down but will keep your server very busy and hence will take more time to accomplish any action. Since you pay for usage with cloud hosting, your costs can spin wildly out of control.
5)Sometimes frustrating: Exploration of next-generation IT models requires a thrill-seeking strength of mind and technical perspicacity. If anyone don’t have the human capital that’s willing to stretch and learn new things, in that scenario, cloud computing becomes very frustrating for them.
Going through the pros and cons of cloud computing, you must have noticed that from operation and maintenance point-of-view cloud computing is a great and cost-effective IT solution for business of any magnitude, but when it is taken from the security and privacy point of view, it still requires lots of time to become a mature system as a reliable and cost-effective computing technology.
Characteristics
Cloud computing exhibits the following key characteristics:
1) In cloud computing environment, performance is monitored and consistent and loosely coupled architectures are constructed using web services as the system interface.
2) Device and location independence enable users to access systems using a web browser regardless of their location or what device they are using e.g., PC, mobile phone. This is especially important when looking for mobile workforce and field service management solutions.
3) There is improved security due to centralization of data, increased security-focused resources, etc. Security is often as good as or better than under traditional systems. However, the complexity of security is greatly increased when data is distributed over a wider area or greater number of devices and in multi-tenant systems that are being shared by unrelated users.
4) Maintenance of cloud computing applications is easier, because they do not need to be installed on each user’s computer.
5) Application Programming Interface (API) accessibility to software enables machines to interact with cloud software in the same way the user interface facilitates interaction between humans and computers.
Architecture
When we talk of cloud computing, its architecture suddenly comes in our mind. We start thinking of how the cloud computing service is operated, how its architecture co-ordinates etc. By the term Cloud architecture, we mean the systems architecture of the software systems involved in the delivery of cloud computing, which typically involves multiple cloud components communicating with each other over loose coupling mechanism such as messaging queue. The success rate of cloud computing is fundamentally based on the effective implementation of its architecture which does not reveal only how the application will work with the intended users but also requires an intricate interaction with the hardware which is quite essential to ensure uptime of the application. Let us see the logical diagram of cloud computing architecture.
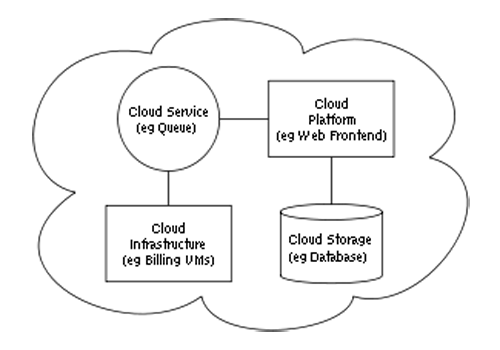
As we know any application comprises of two sections: the front end and the back end. To connect front end with back end an Internet connection is usually needed. By front end, we mean the side the computer user, or client sees and by back end we mean the “cloud” section of the system. And whatever the data is communicated is needs a storage space that is called as database storage. Now let us see how these co-ordinates among each other. The front end constitutes of the client’s computer or computer network and the application required to access the cloud computing system. On the other side, back end of the system are the various computers, servers and data storage systems that create the “cloud” of computing services. Theoretically, a cloud computing system could include practically any computer program ranging from data processing to video games. Now, each application will have its own dedicated server and a central server administers the system, monitoring traffic and client ensuring everything to run in a smooth manner which in turn follows a set of rules called protocols and uses a special kind of software called middleware; Middleware allows networked computers to communicate with each other.
The below given diagram will explain the architecture of Cloud computing in more detail.
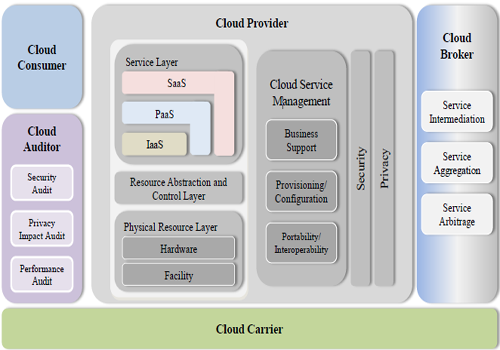
When you will carefully look over the above diagram you will find that, the entire architecture revolves itself around user roles for cloud computing. On either end, you have the cloud service creator/broker and cloud service consumer. As its name implies, the cloud service broker role includes any type of cloud service dealing tools. These tools include software development environments, virtual image development tools, process choreographing solutions, and anything else a developer may use to create services for the cloud. On the other side of the architecture, the cloud service consumer comes into focus. The architecture above accounts for in-house IT as well as cloud service integration tools as consumers.
Finally, in the middle of the diagram, we have perhaps the most complex role, the cloud service provider. This section addresses two basic facets for providers: services and service management. From a services perspective, we see the trinity of the cloud (IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS). Opposite the services, we see the common management framework that accounts for those capabilities that a provider needs to effectively operate a cloud environment and to support the business requirements of cloud.
Other functional requirements that span all three roles including security, performance, resiliency, consumability, and governance are dealt in with Cloud Auditor section of the architecture shown above.
Layers
Cloud Computing has five different layers, one after the other. These are:
1. Client
2. Application
3. Platform
4. Infrastructure, and,
5. Server
Once an Internet Protocol connection is established among several computers, it is possible to share services within any one of the following layers. The functionality of each layer of cloud computing is discussed below.
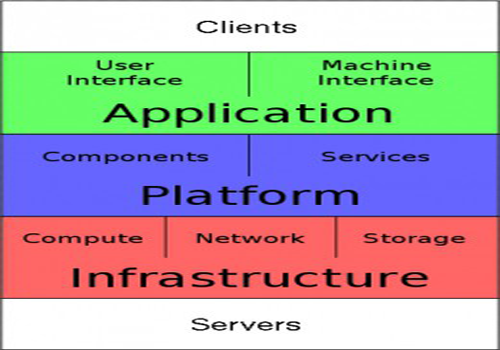
1) Clients: It is the first layer of cloud computing which consists of computer hardware and/or computer software that relies on cloud computing for application delivery and that is in essence useless without it. Examples include some computers, phones and other devices, operating systems, and browsers etc.
2) Application: This layer also referred as the Cloud application services or Software as a Service (SaaS) deliver software as a service over the Internet, eliminating the need to install and run the application on the customer’s own computers and in this way simplifying maintenance and support.
3) Platform: This layer also known as Cloud platform services or Platform as a Service (PaaS), deliver a computing platform and/or solution stack as a service, often consuming cloud infrastructure and sustaining cloud applications. It facilitates deployment of applications without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers.
4) Infrastructure: This layer facilitates Cloud infrastructure services, also known as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), and delivers computer infrastructure typically a platform virtualization environment as a service, along with block storage and networking. Clients buy those resources as a fully outsourced service rather than purchasing servers, software, data-center space or network equipment. Suppliers typically bill such services on a utility computing basis; the amount of resources consumed and hence the cost incurred typically reflects the level of activity.
5) Server: It is the fifth and last layer of Cloud computing architecture and consists of computer hardware and/or computer software products that are specifically designed for the delivery of cloud services, including multi-core processors, cloud-specific operating systems and combined offerings.
Conclusion
Cloud computing can be more considered as an emerging technology as it is not only becoming one of those buzz words of the moment but in reality, this low-cost computing power is gaining popularity among businessmen, especially medium and small size, and governmental organizations, as people are realizing the power of cloud environments to a great extent. That is why there are many different applications that use these environments, such as financial applications like an enterprise cloud for larger businesses.” Going through the above contents one thing must have become clear to you that cloud computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resource, i.e. networks, servers, storage, applications, and services that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction.
Although, Cloud Computing suffers some serious security and privacy related problems, despite this, it is a lucrative choice to improve productivity in any business environment, where IT is in high demand. Now with cloud computing, you don’t have to worry about software updates, installation, email servers, anti-viruses, backups, web servers and both physical and logical security of your data and in this way it assists you to focus more on your core business competency making you free from all worries.
